This guide refers to PCB version 1.07.
If you have a v1.04 board, please refer to this guide.
Needed tools
You will need the following tools for this build:
- 1x 15-25W soldering iron
- Some solder (60/40 leaded solder is recommended as it is easier to work with – just wash your hand after soldering and you’ll be safe)
- A basic digital multi meter (DMM) to check for voltage and shorts
- Optionally, a piece of desoldering braid and a solder sucker pump can be handy if desoldering a part is needed
- Some patience
What comes with the kit?
In the kit, you will find
- PCB
- BRAIN40 board (CPU)
- Soldered DAC
- 2×24 LCD screen
- Active parts bag
- Passive bag
- Misc bag (pot, encoders, knobs, buttons, etc.)
If you did buy an acrylic case with your kit, you additionally have the acrylic panels and a bag of screws and spacers.
Before you start
Building P6 is easy if you’re used to soldering. If you’re new to this, I recommend reading this tutorial.
Please also check this page that will help you identify bad solder joints.
Take your time, read this guide twice before warming your soldering iron.
Work in a clean place with enough space to do things properly.
Take your time and be patient, you will have a fully functional synth if you follow this guide thoroughly , but a single little mistake can turn a few hours build into a days/weeks build.
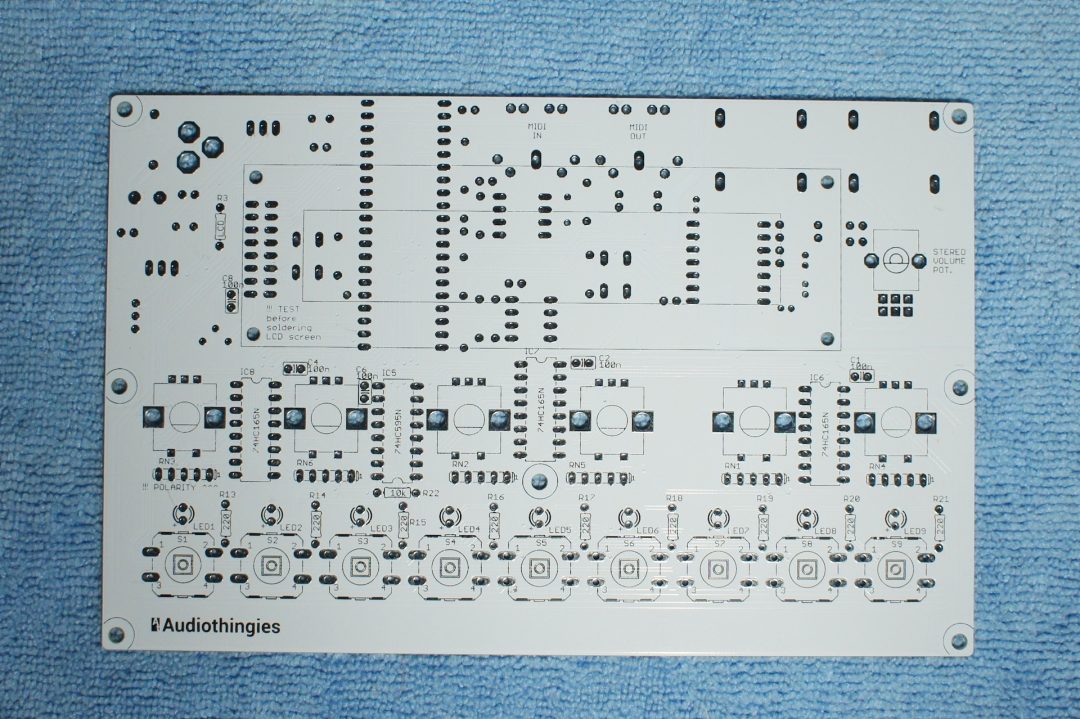
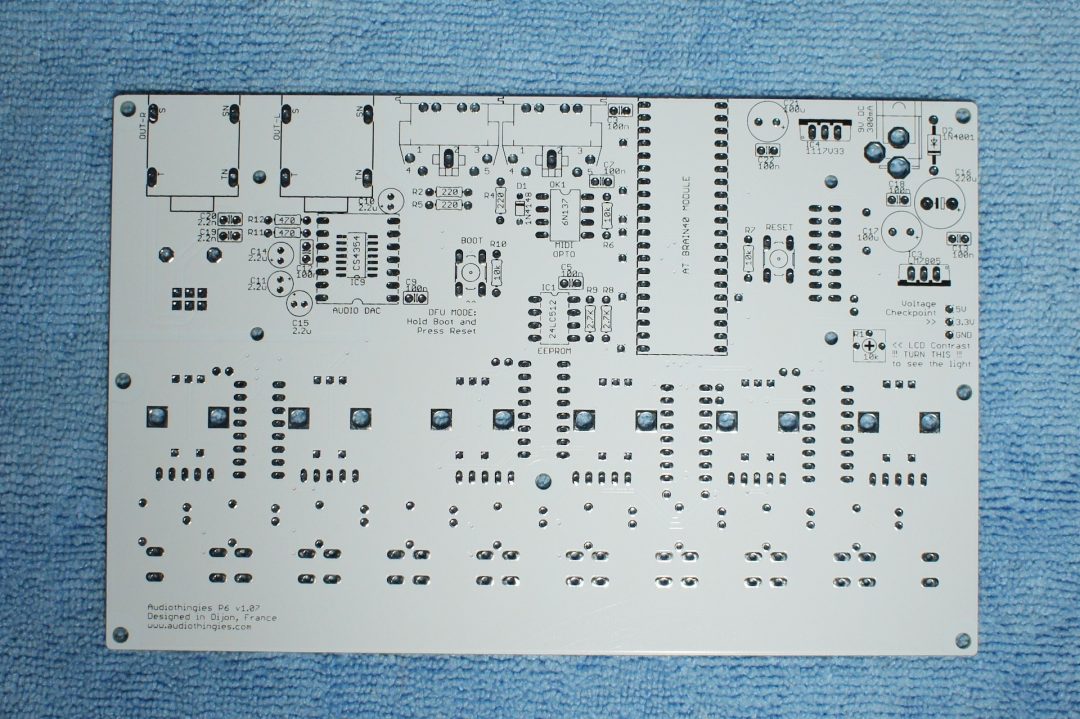
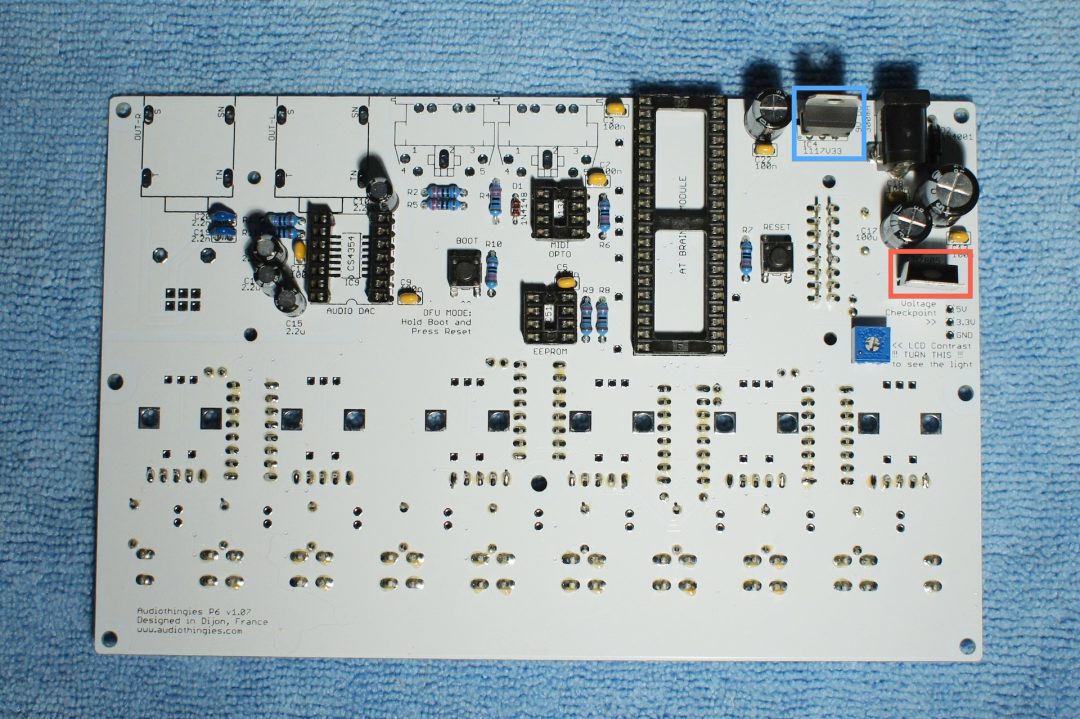
The bare PCB
Here are 2 pics of the P6 bare PCB (version 1.07)
Step 1
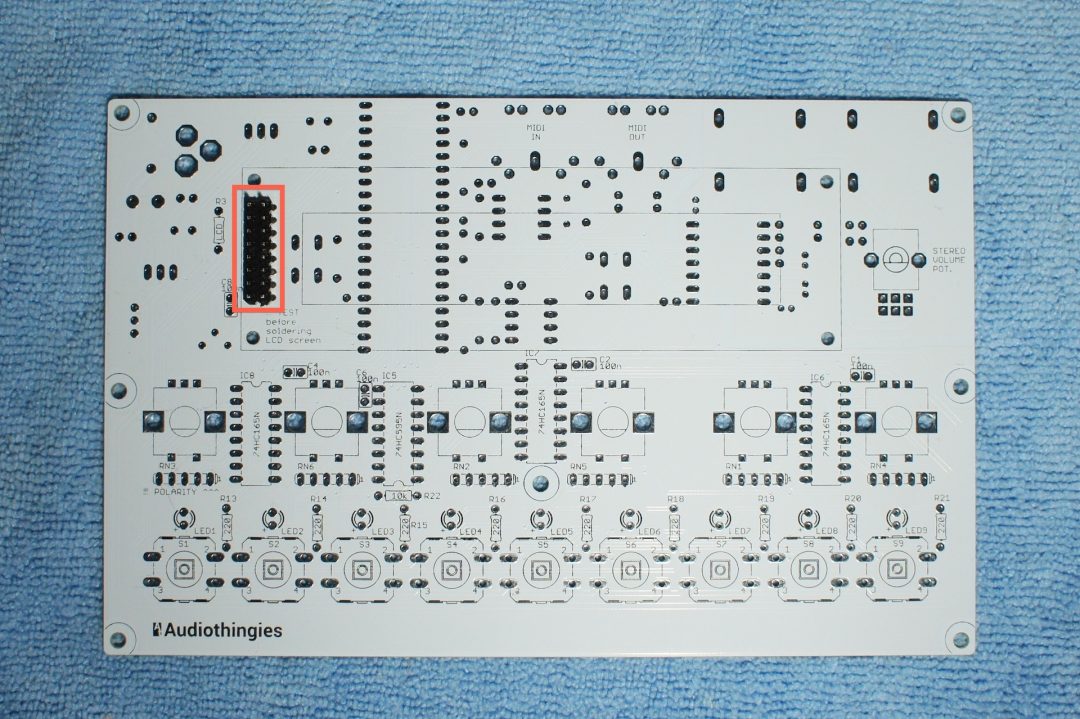
We will start by soldering the LCD pin headers (longest lead thru the pcb), as it can be difficult to solder it later.
Step 2
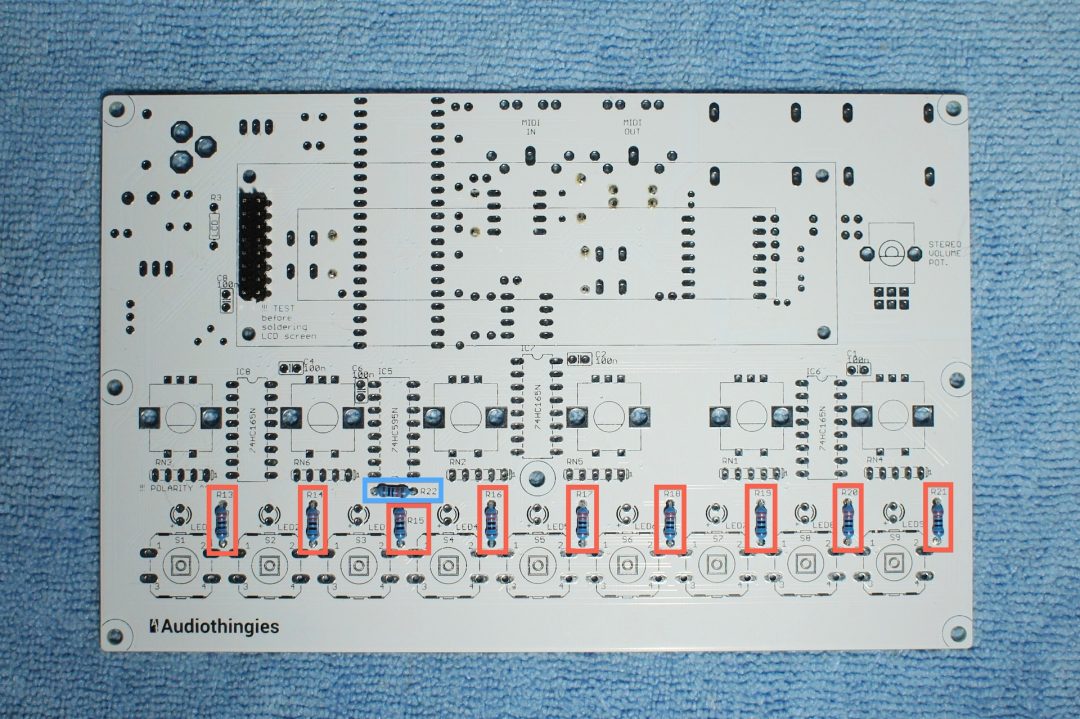
Solder these resistors:
– R13 to R21 (220 ohms : Red Red Brown Brown or Red Red Black Black Brown)
– R22 (10k ohms : Brown Black Orange Brown or Brown Black Black Red Brown)
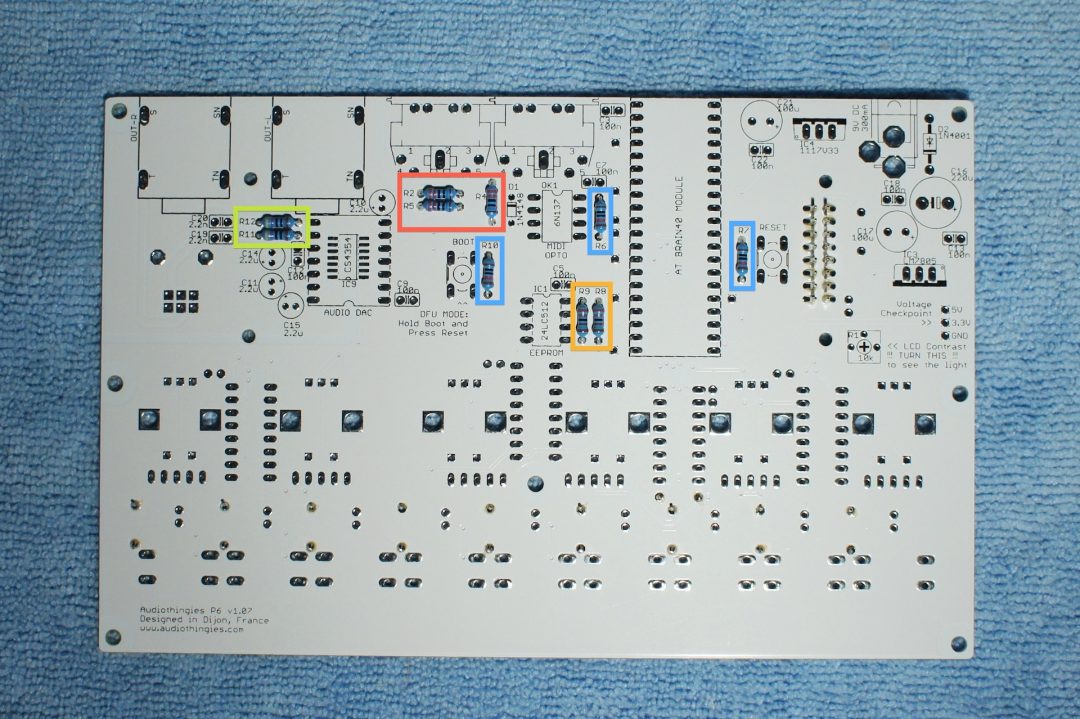
– R2, R4, R5 (220 ohms : Red Red Brown Brown or Red Red Black Black Brown)
– R6, R7, R10 (10k ohms : Brown Black Orange Brown or Brown Black Black Red Brown)
– R8 and R9 (2.7k ohms : Red Violet Red Brown or Red Violet Black Brown Brown)
– R11, R12 (470 ohms : Yellow Violet Brown Brown or Yellow Violet Black Black Brown)
Step 3
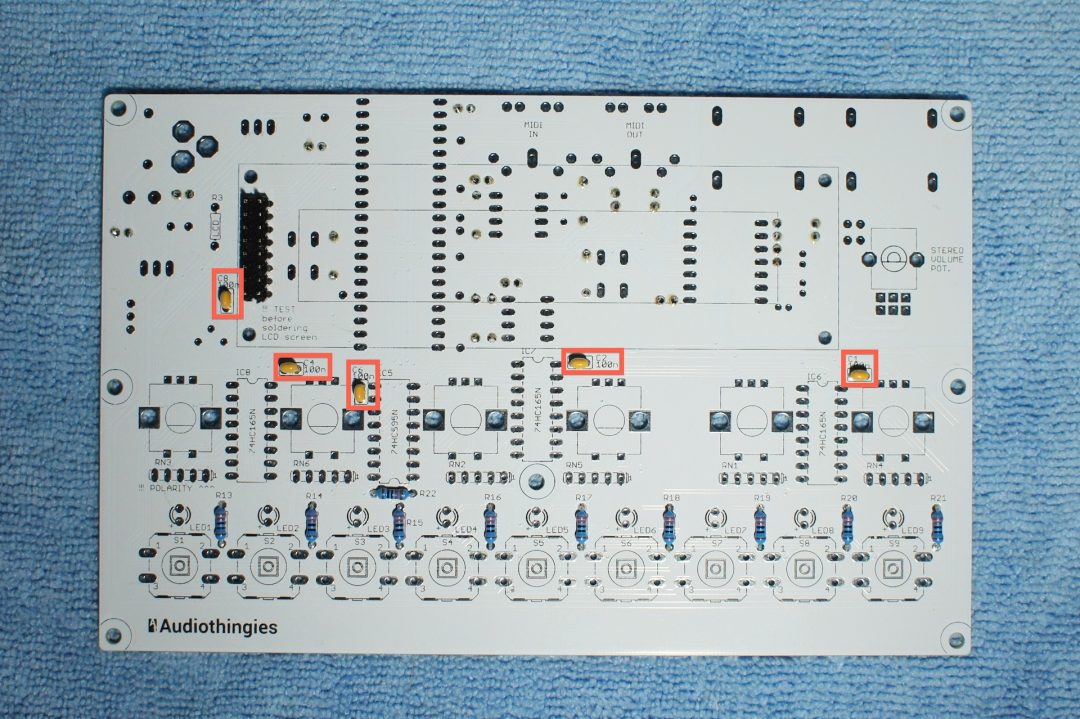
Install the 100nF caps (marked 104).
These are not polarized.
Top side
– C1, C2, C4, C6, C8
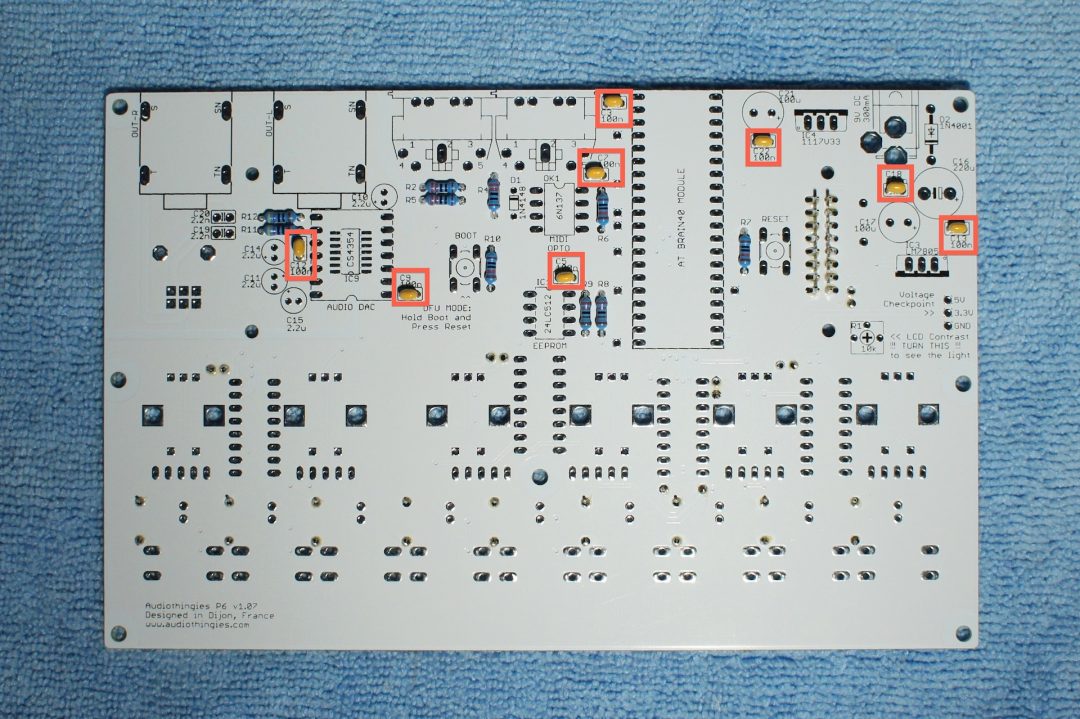
Bottom side
– C3, C5, C7, C9, C12, C13, C18, C22
Step 4
Solder C19 and C20 (2200p : marked 222). Those 2 are not polarized.
And R1, the LCD screen contrast pot
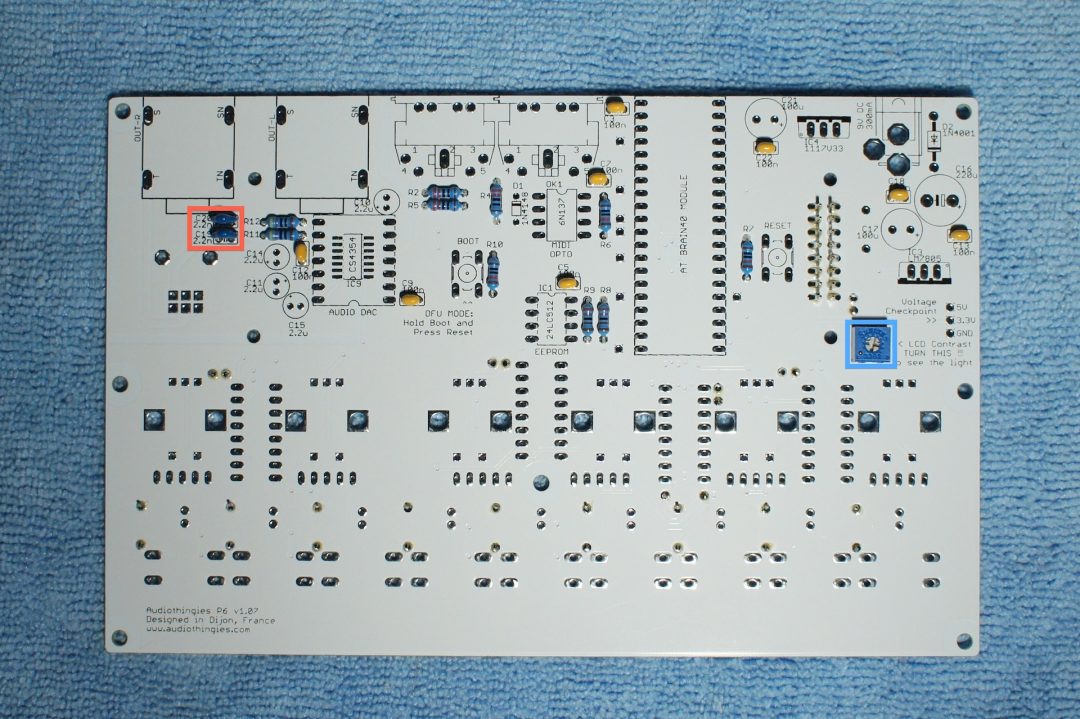
Step 5
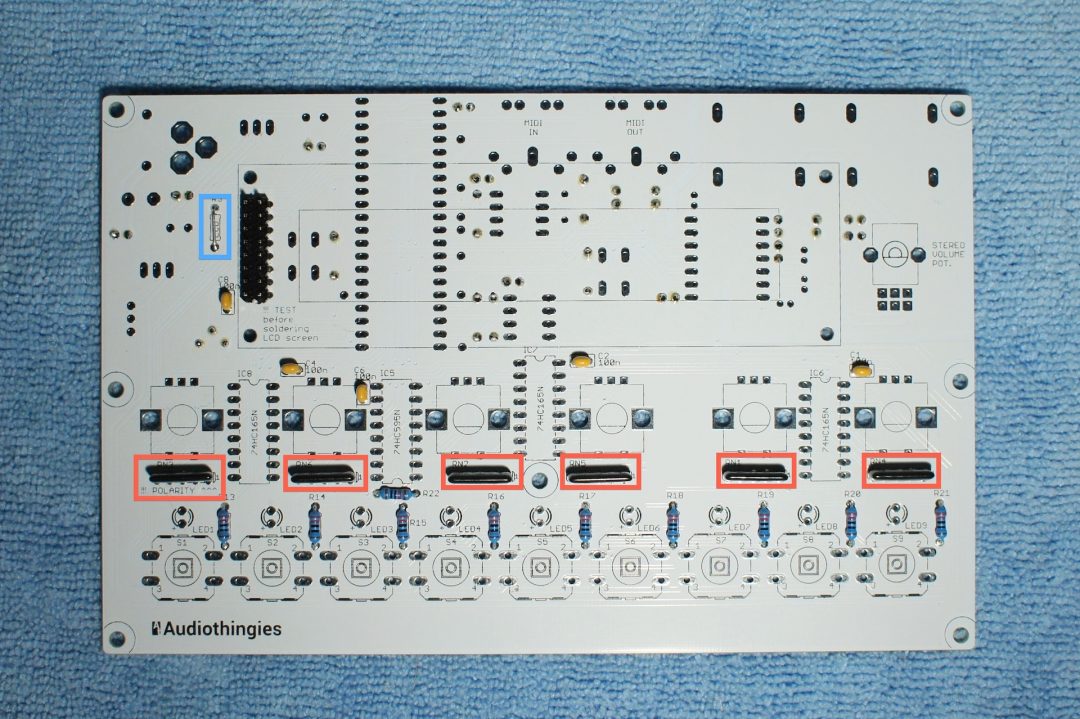
Resistors again
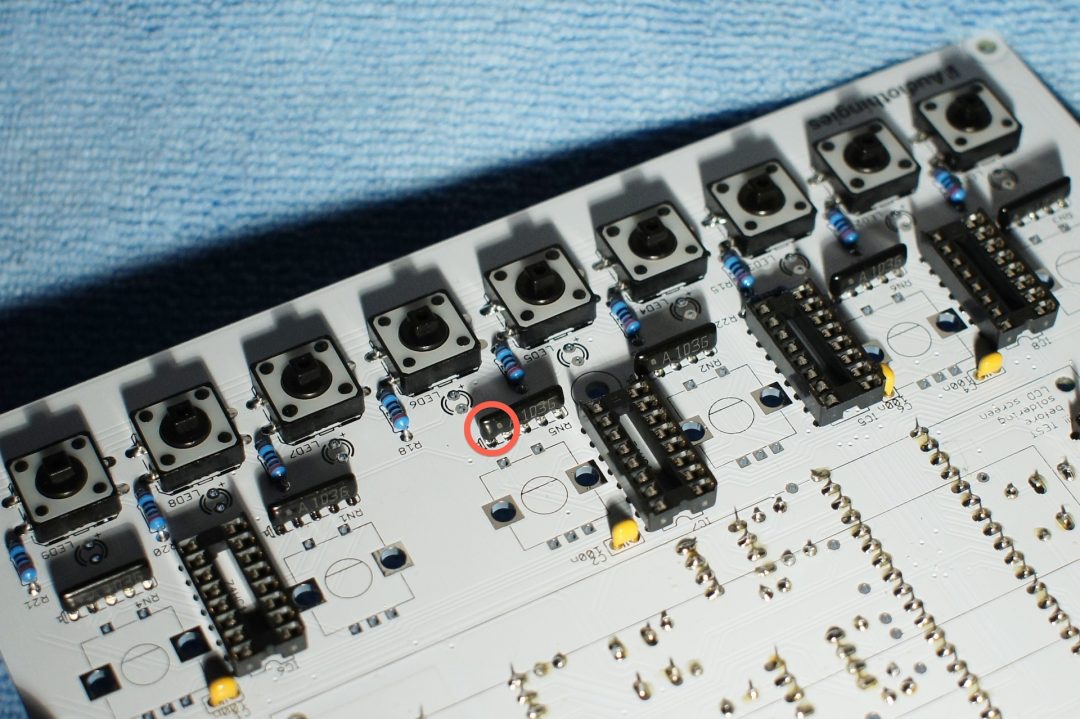
– R3: if you use the lcd provided in the kit, install a jumper in R3 (not provided in the kit, use a lead of a component you just cut)
– RN1 to RN6: resistor networks. These are polarized. The side with a white stripe points to the right of the pcb (indicated with a little 1 on the silkscreen).
Also look for the close up in step 7 that should help getting the right orientation for the resistor networks.
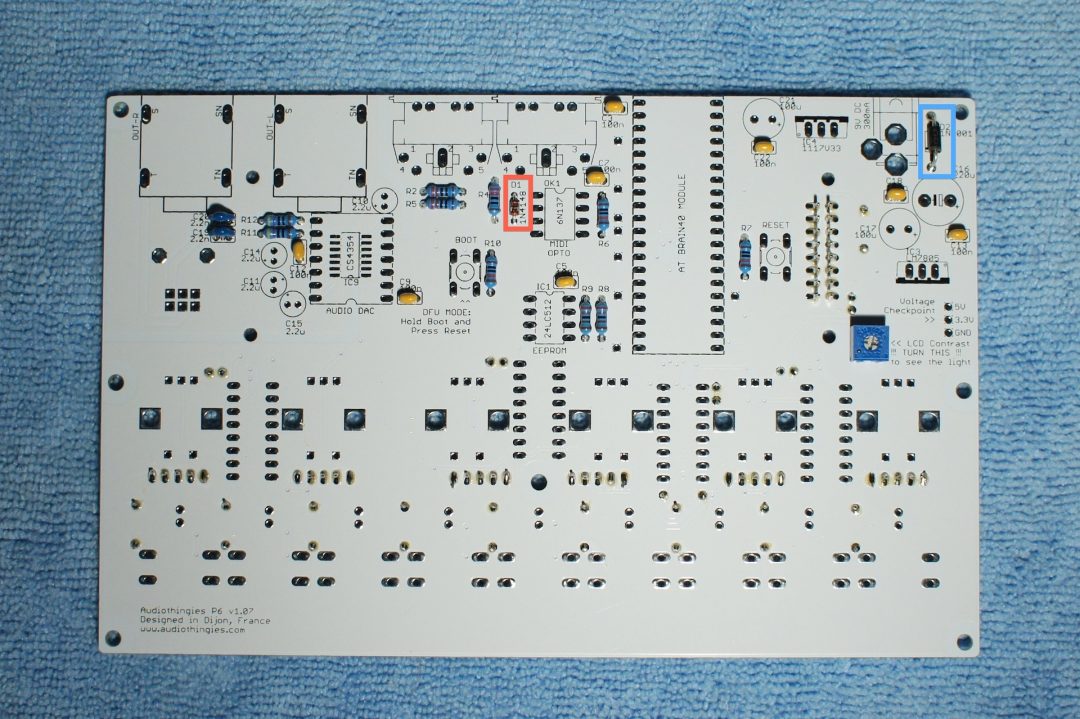
Step 6 – Diodes
These are polarized. Pay attention to the orientation. They are 2 diodes :
– D1 (1N4148) – black ring point to the MIDI connector
– D2 (1N4001) – grey ring point to C16
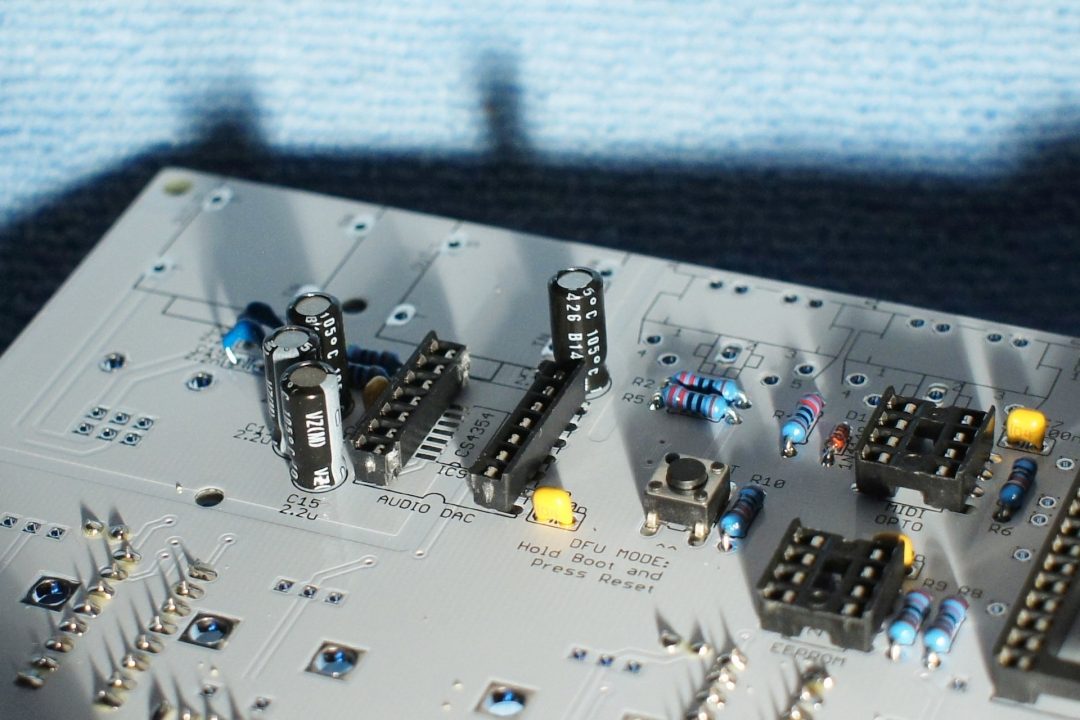
Step 7
Install the switches and the IC sockets.
Notice the orientation of the IC sockets.
Top side
Bottom side
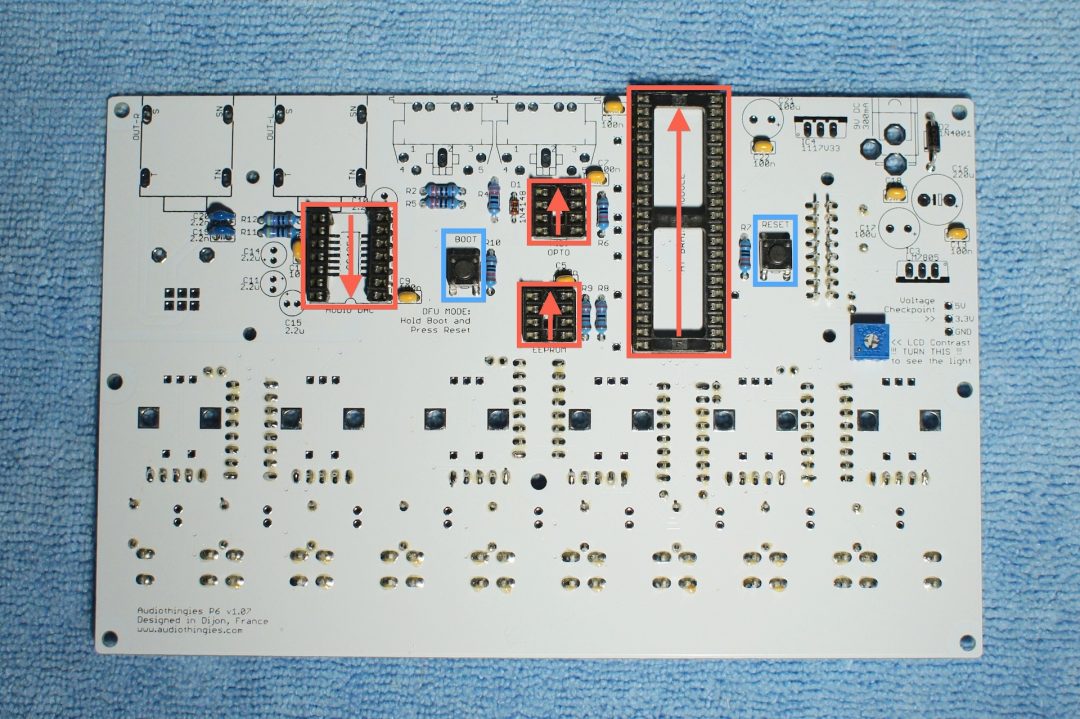
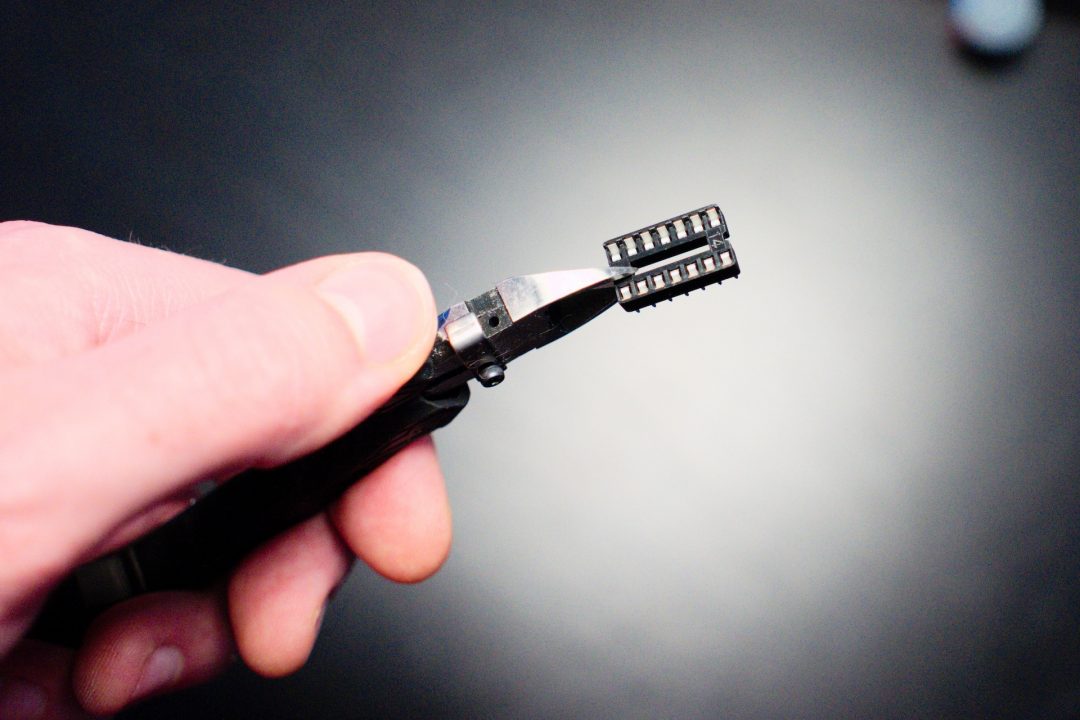
To install the DAC 14-pin socket, you need to cut a standard 14-pin IC socket into 2 pieces, like this:

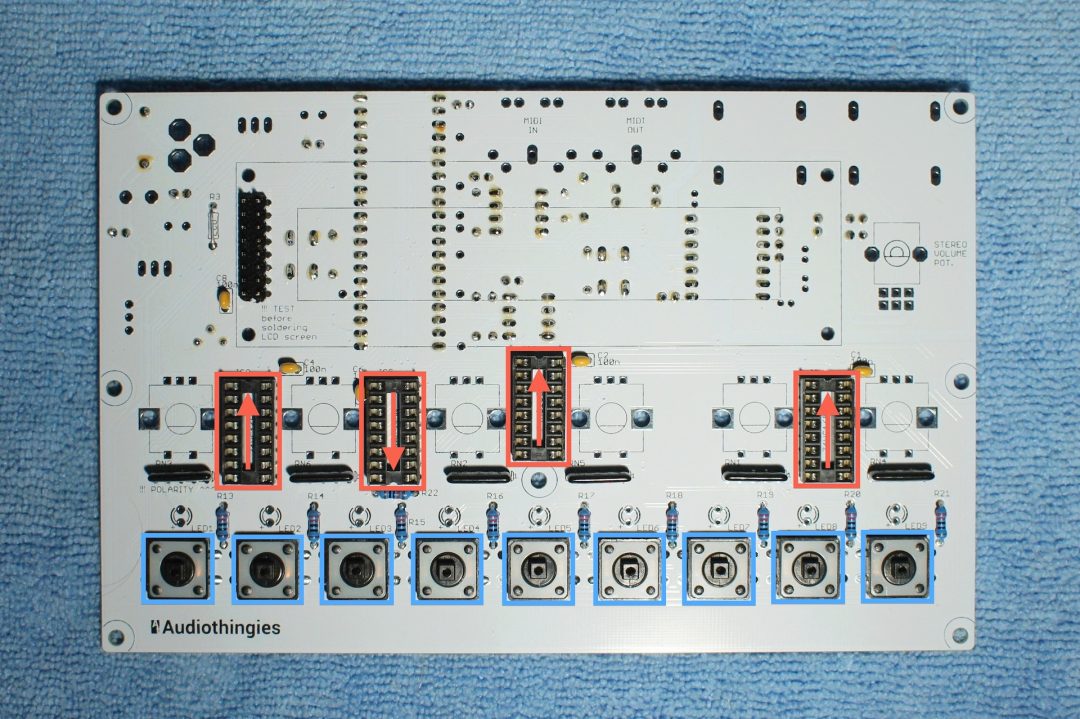
Here is a close-up of the top side.
Notice the resistor network orientation.
Step 8
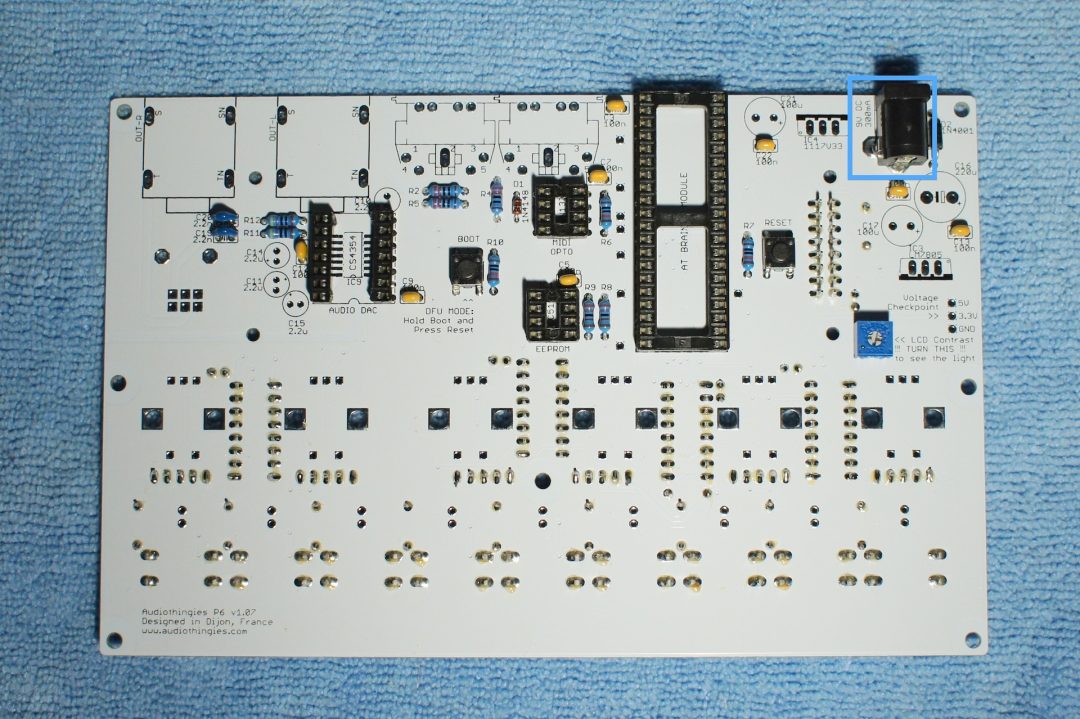
Instal the DC connector
– J1 : Solder one leg, adjust the connector into the right position, then solder the other legs.
Step 9
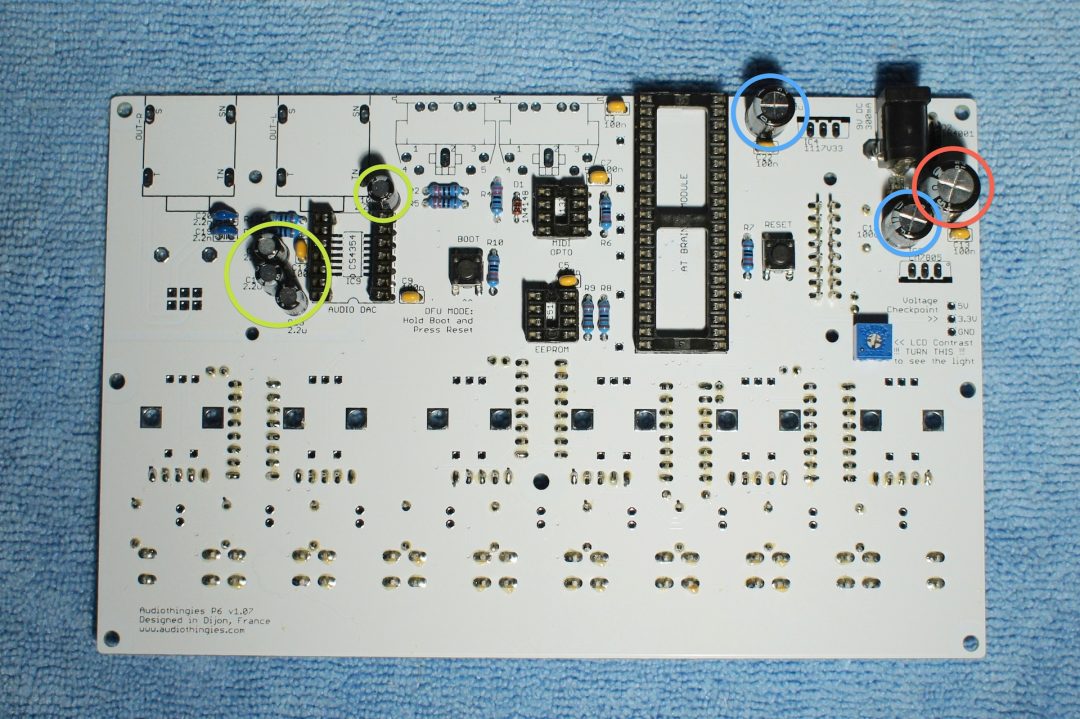
Solder the electrolytic capacitors
The white stripe on the side of the electrolytic capacitors indicates the negative lead. The negative lead is the shortest one. This means the longest lead (positive) must go in the hole marked with a plus sign. Quite logical after all…
Power supply section (right side of board):
– C17, C21 (100u)
– C16 (220u)
Audio section (left side):
– C10, C11, C14, C15 (2.2u)
Also look at step10 close ups to check for the correct orientation.
Step 10
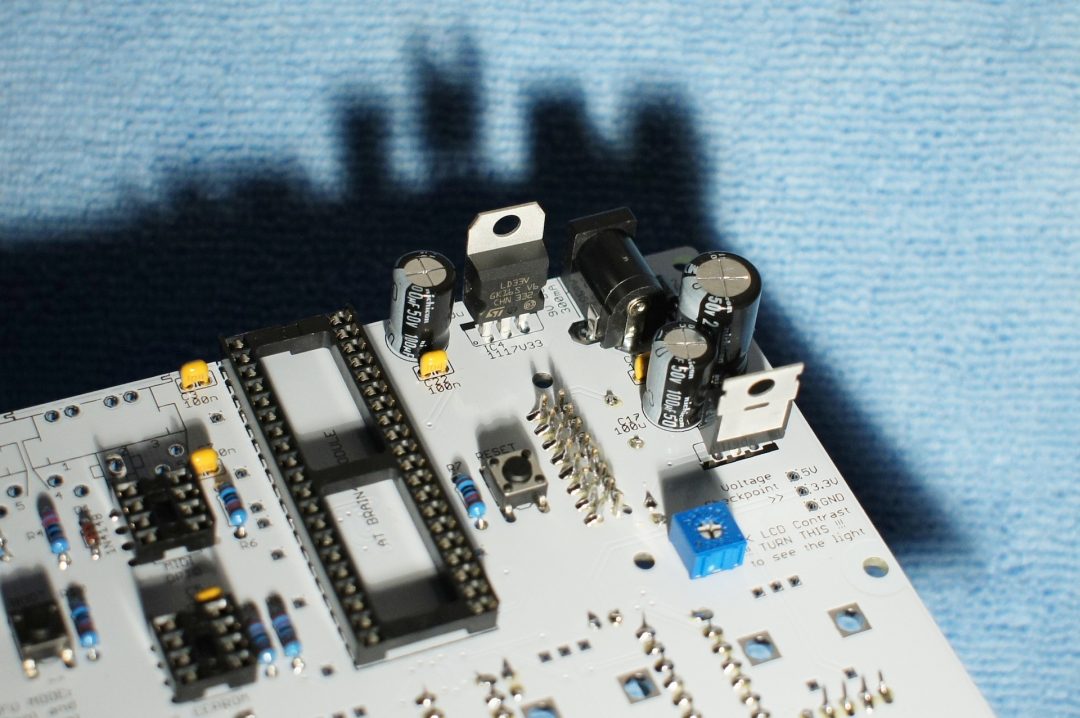
The board needs 2 different voltages, 5V and 3.3V.
Install the 2 voltage regulators
– IC3: 7805 “metal” plate points to the bottom of the board.
– IC4: 1117V33 or LD33CV “metal” plate points to the top of the board
Do not invert the 2 voltage regulators, they look the same but they are not the same!
Close up 1
Close up 2
At this point, look for short cuts between +5V, +3.3V and ground.
GND, 3.3V and 5V test points are available at the right side of this PCB side.
Check cap polarity again.
If OK, without any IC’s inserted, power the board and control the voltages using the same test points. You should read 5V (4,95 – 5,05) and 3.3V (3,25 – 3,35).
Step 11
Install and solder the Audio / MIDI connectors

Step 12
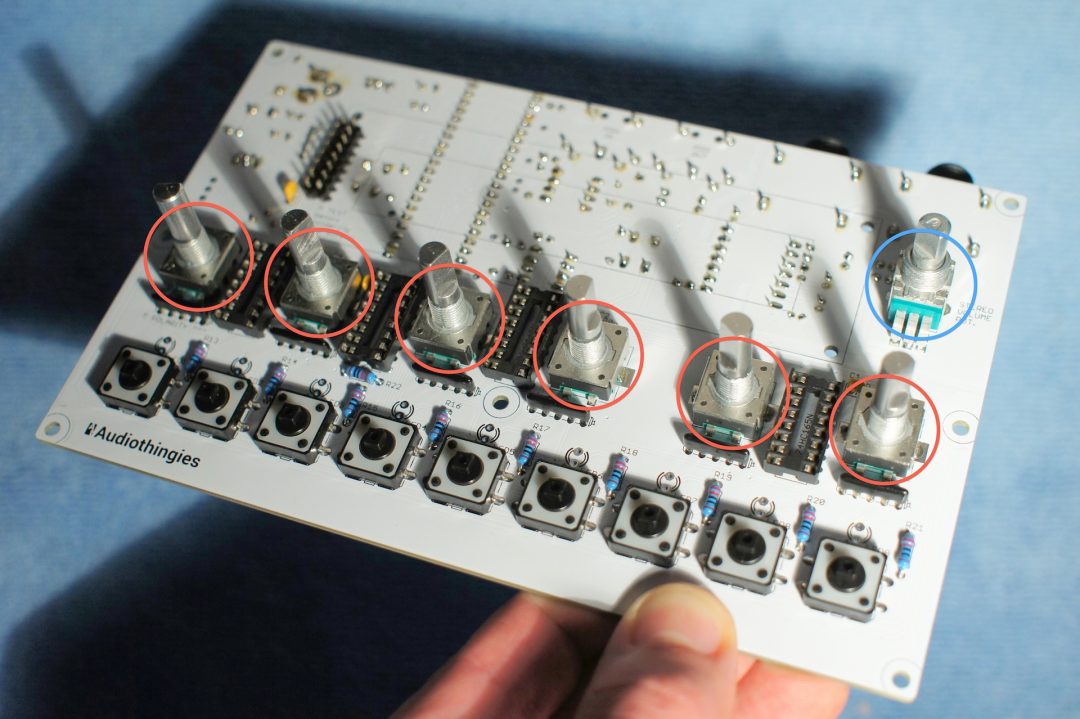
Pots and encoders
You can remove the anti-rotation tag on the stereo volume pot with a pair of pliers.
Step 13
It’s time to insert all IC’s for a first test.
Pay attention to the chips orientation – that should be clear enough on the 2 following pics.
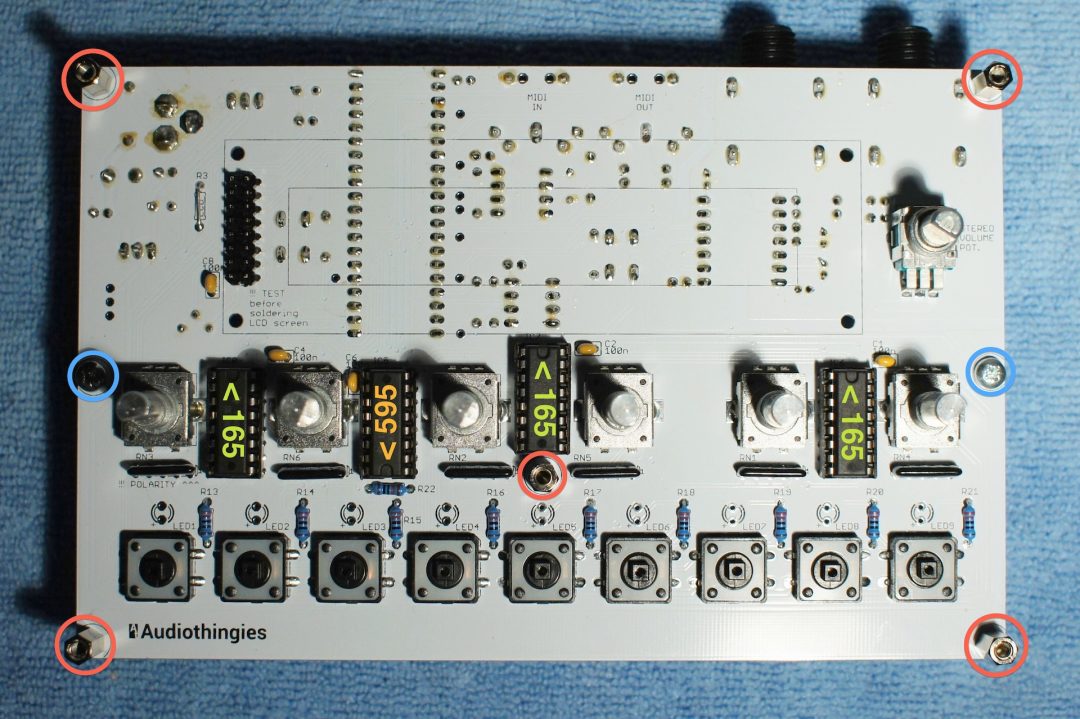
You can also install spacers at this step
Top side
Red: MF 10mm M3 spacer
Blue: M3x6 screw
Green: 74HC165
Orange: 74HC595
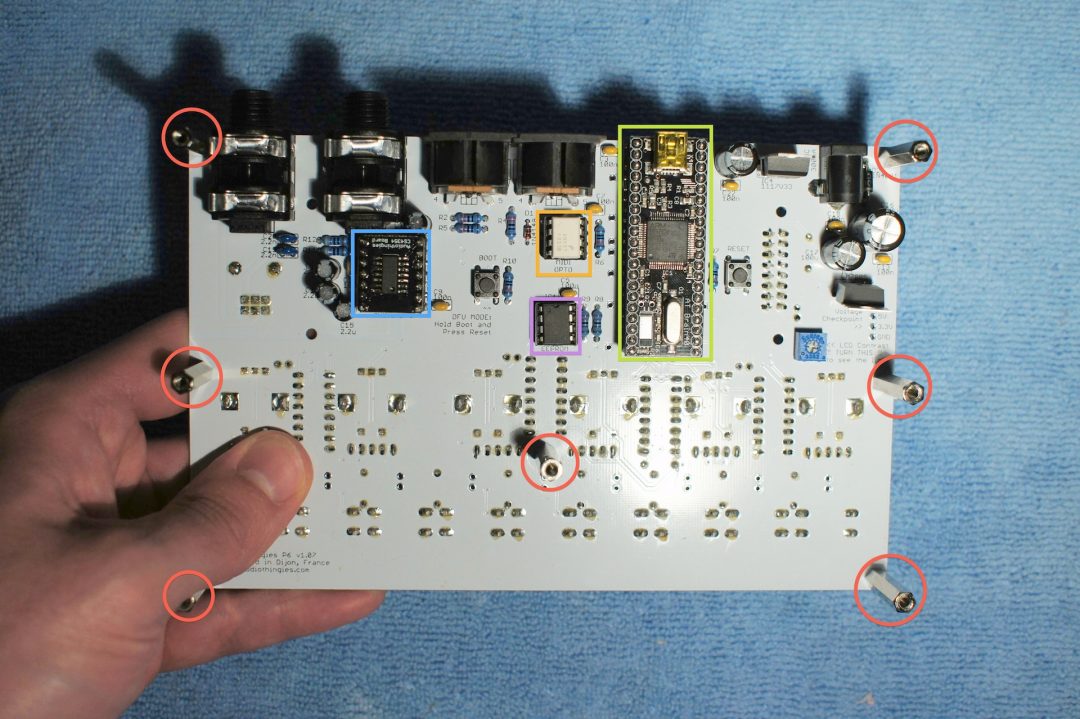
Bottom side
Red: FF 25mm M3 spacer
Blue: DAC board
Yellow: Brain40 board
Orange: 6N137 (can be black in some kits)
Violet: 24LC512 EEPROM
Step 14
Power the board with a 9V DC adapter.
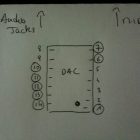
Measure the voltages on the DAC.
Here is the pin numbering for the DAC (click to enlarge)
Measured values on my prototype are :
- 1 : 3,3V
- 6 : 0V (check continuity with GND)
- 7 : 3,5V
- 10 : 0V (check continuity with GND)
- 11 : 5V
- 12 : 2,55V
- 13 : -2,4V
- 14 : -4,8V
If you do not have these voltages, double check your soldering on the DAC pins and surrounding caps.
Then, if all good, connect a MIDI keyboard (channel 1) to MIDI IN socket (the one that is next to the mini-USB port), audio outs to a mix table.
Play a few notes, you should hear a basic sound responding to pitch (don’t forget to turn the pot volume up – I always do).
If you have the sound, then everything’s fine. Do not try to load any presets as this will not work yet.
If not, then triple check your voltages, solder joints, IC orientations until you get a sound.
DO NOT GO BEYOND THIS POINT IF YOU HAVE NO SOUND OR WRONG VOLTAGES – ASK FOR HELP ON THE FORUMS
Step 15
Place and screw the LCD screen with the included M2.5x10mm screws and nuts, with a 3mm nylon spacer between the LCD and the board.
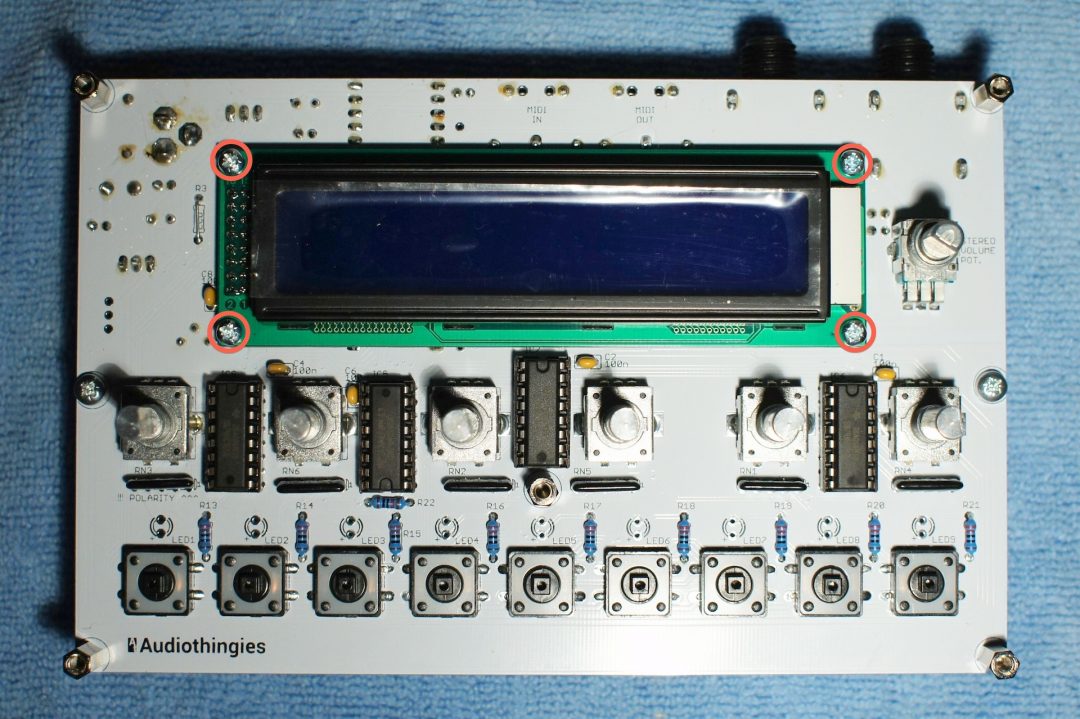
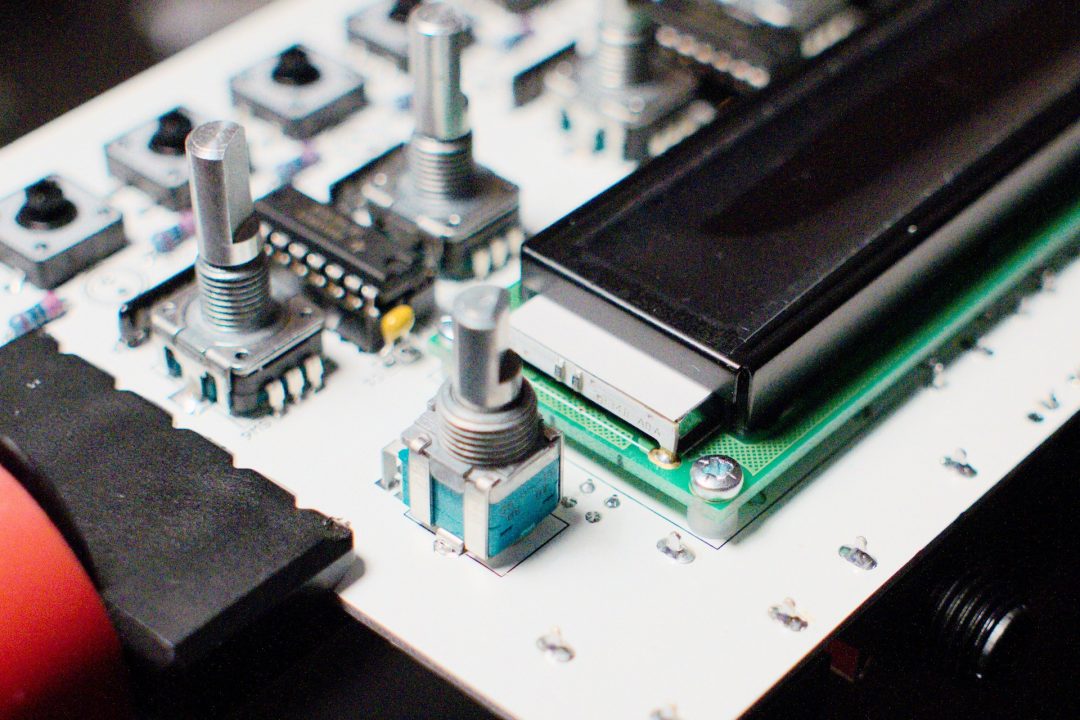
Do not solder the lcd yet.
Check if you still have sound with a MIDI keyboard. If not, you may have a short between the board and the lcd.
When everything’s fine, solder the LCD.
Power the unit again, you should have the LCD working.
Step 16
It’s time to format the EEPROM:
Power the unit while pressing buttons 2 and 8.
A screen will appear asking for an EEPROM Format.
Press Load to confirm. This will also write a few presets to get you started.
Step 17
Insert the LEDs without soldering them. The longest lead (positive side) is on the side of the switch (indicated with a + sign on the silkscreen)
Re-check polarity, longest lead (positive side) is on the side of the switch, not the encoder.
Mount and screw the top panel with M3 black hex screws.
Return the unit.
Slip the LEDs into their respective holes and solder them. This ensures the LEDs fit perfectly in their respective holes.
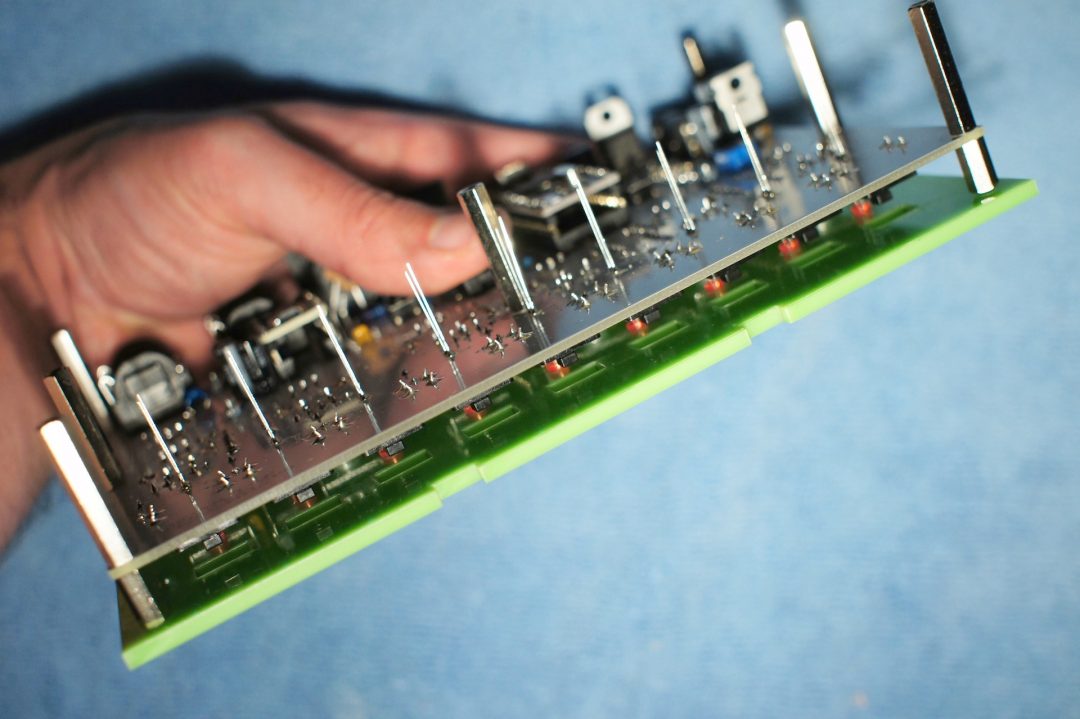

And here’s the result: perfectly aligned LEDs
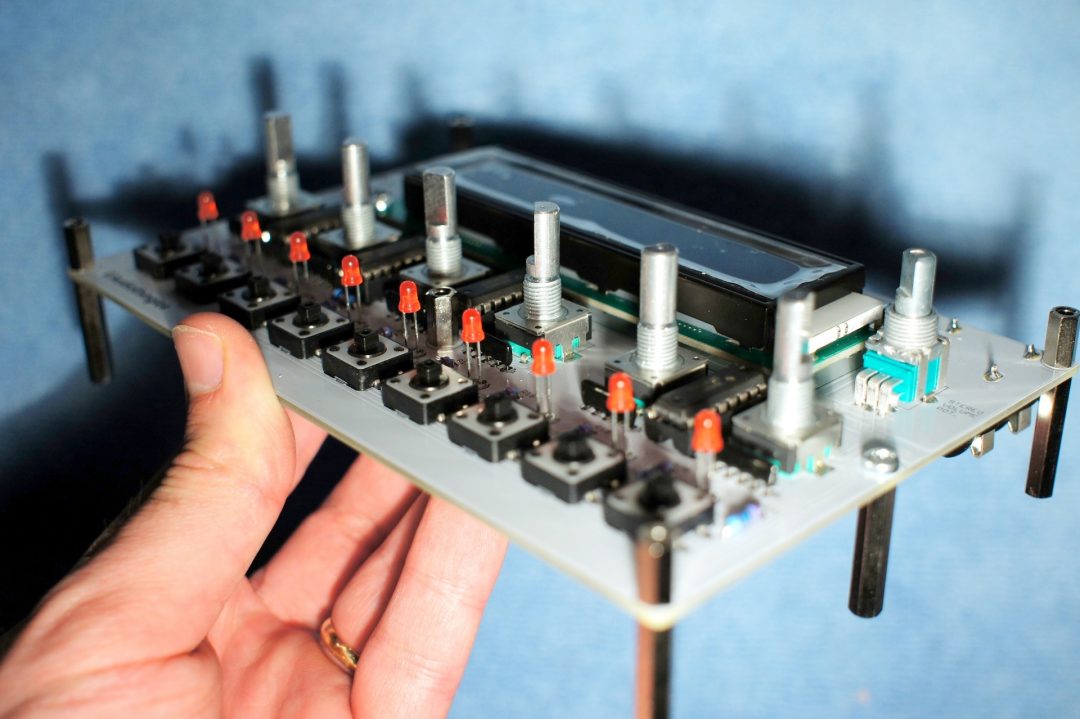
Step 18
Power the board again, you should have LCD working, LEDs working and sound output.
Play a bit with the P6 and check that everything’s working, buttons, encoders, etc… before mounting the unit into a case.
Step 19
To assemble the case, we recommend the following sequence:
- Mount and tighten the top panel with 4 M3 black hex screws
- Add the encoder and pot knobs
- Mount the bottom panel with the remaning 7 black hex M3 screws – do not tighten the screws yet
- Place the 4 side panels, add the audio jack nuts
- Tighten the 7 bottom panel hex screws
- The side panels are secured with M2.5x12mm black screws and nuts.
Step 20
Congratulations! It’s time for the Victory Candy!
Now you can update your P6 to the latest version.